International human rights treaties
Besides the adoption in 1966 of the two wide-ranging Covenants that form part of the International Bill of Human Rights (namely the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights), other treaties have been adopted at the international level. These are generally known as human rights instruments. Some of the most significant include the following:
- the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide (CPCG) (adopted 1948 and entered into force in 1951);
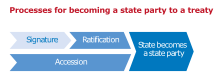 Processes for becoming a state party to a treaty
Processes for becoming a state party to a treaty - the Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees (CSR) (adopted in 1951 and entered into force in 1954);
- the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (CERD) (adopted in 1965 and entered into force in 1969);
- the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) (entered into force in 1981);
- the United Nations Convention Against Torture (CAT) (adopted in 1984 and entered into force in 1987);
- the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) (adopted in 1989 and entered into force in 1990);
- the International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of their Families (ICRMW) (adopted in 1990 and entered into force in 2003);
- the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) (entered into force on 3 May 2008); and
- the International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearance (ICPPED) (adopted in 2006 and entered into force in 2010).

Comments
Post a Comment